Traducción y análisis de palabras por inteligencia artificial ChatGPT
En esta página puede obtener un análisis detallado de una palabra o frase, producido utilizando la mejor tecnología de inteligencia artificial hasta la fecha:
- cómo se usa la palabra
- frecuencia de uso
- se utiliza con más frecuencia en el habla oral o escrita
- opciones de traducción
- ejemplos de uso (varias frases con traducción)
- etimología
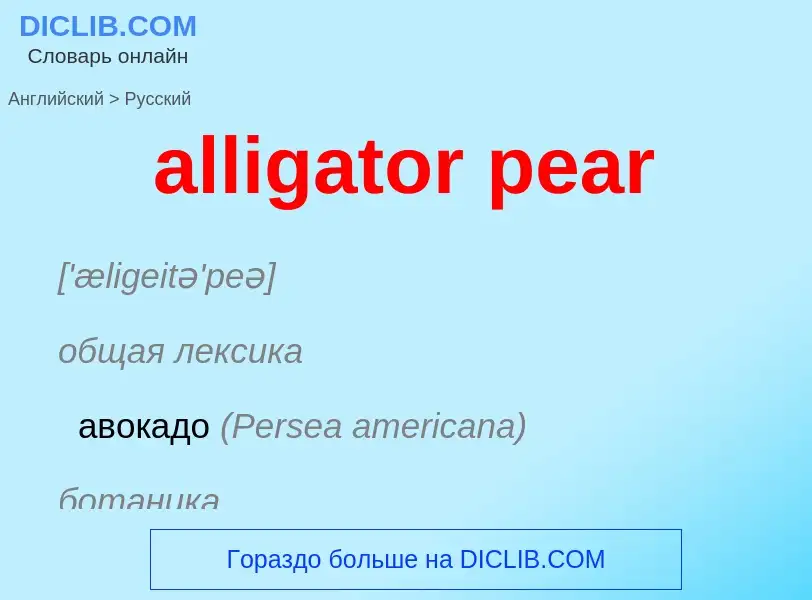
alligator pear - traducción al ruso
['æligeitə'peə]
общая лексика
авокадо (Persea americana)
ботаника
аллигаторова груша (Persea gratissima)
аллигаторова груша
[ævə'kɑ:dəu]
общая лексика
авокадо (Persea gratissima)
существительное
общая лексика
плод авокадо
ботаника
авокадо
аллигаторова груша (Persea gratissima)
Wikipedia
The avocado (Persea americana) is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Then as now it was prized for its large and unusually oily fruit. The tree likely originated in the highlands bridging south-central Mexico and Guatemala. Its fruit, sometimes also referred to as an alligator or avocado pear, is botanically a large berry containing a single large seed. Avocado trees are partly self-pollinating, and are often propagated through grafting to maintain consistent fruit output. Avocados are presently cultivated in the tropical and Mediterranean climates of many countries. Mexico is the world's leading producer of avocados as of 2020, supplying nearly 30% of the global harvest in that year.
The fruit of domestic varieties have smooth, buttery, golden-green flesh when ripe. Depending on the cultivar, avocados have green, brown, purplish, or black skin, and may be pear-shaped, egg-shaped, or spherical. For commercial purposes the fruits are picked while unripe and ripened after harvesting. The nutrient density and extremely high fat content of avocado flesh are useful to a variety of cuisines and are often eaten to enrich vegetarian diets.
In major production regions like Chile, Mexico and California the water demands of avocado farms place strain on local sources. Avocado production is also implicated in other externalities, including deforestation and human rights concerns associated with the partial control of their production in Mexico by organized crime. Global warming is expected to result in significant changes to the suitable growing zones for avocados, and place additional pressures on the locales in which they are produced due to heat waves and drought.


![First international air shipment of avocados from Los Angeles to Toronto for the [[Canadian National Exhibition]], 1927 First international air shipment of avocados from Los Angeles to Toronto for the [[Canadian National Exhibition]], 1927](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Special:FilePath/Avocado firstInternationalShipment.jpg?width=200)
![Native [[Oaxaca]] ''criollo'' avocados, the ancestral form of today's domesticated varieties Native [[Oaxaca]] ''criollo'' avocados, the ancestral form of today's domesticated varieties](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Special:FilePath/Criollo avocados de Oaxaca.png?width=200)
![Avocado has elliptical-shaped [[leaves]] Avocado has elliptical-shaped [[leaves]]](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Special:FilePath/Green avocado foliage (Persea americana).jpg?width=200)



![[[Avocado toast]] [[Avocado toast]]](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Special:FilePath/2014 avocado salad tomato salsa toasted baguette.jpg?width=200)
![Avocado in milk and sugar]], a traditional dish from the Philippines where avocados are regarded as a dessert fruit, rather than savory. Avocado in milk and sugar]], a traditional dish from the Philippines where avocados are regarded as a dessert fruit, rather than savory.](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Special:FilePath/Avocado lamaw (Avocado in milk and sugar, chilled or with ice), Philippines 04.jpg?width=200)
![A [[guacamole]] mix (right) used as a dip for [[tortilla chip]]s (left). A [[guacamole]] mix (right) used as a dip for [[tortilla chip]]s (left).](https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Special:FilePath/Guacomole.jpg?width=200)

 variety from Cebu Philippines 2.jpg?width=200)
